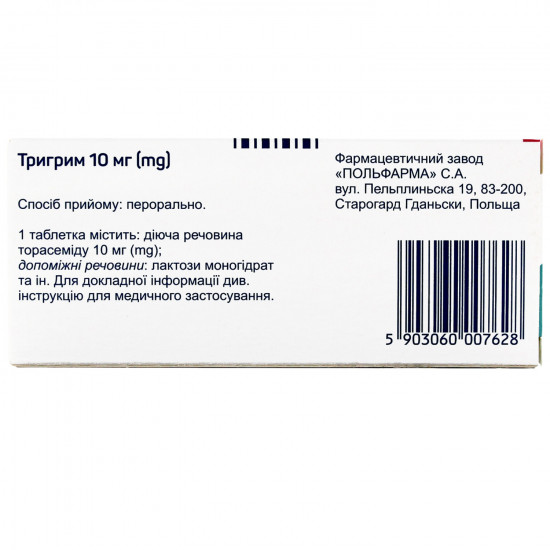



- Stock: In Stock
- Model: 182812
0% Customers recommend this product
-
5 Awesome0%
-
4 Great0%
-
3 Average0%
-
2 Bad0%
-
1 Poor0%
Reviews Over To Trigry tab. of 10 mg No. 30
- (0)
Total Reviews (0)
click here write review to add review for this product.
Report this review.
Description
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics. torasemid — loopback diuretic. at use oppresses a reabsorption of ions of sodium and chlorine in the ascending part of a Henle's loop. antihypertensive action of a torasemid is caused by decrease opss due to normalization of the broken electrolytic balance and mainly decrease of the activity of free calcium in cells of a muscular layer of arteries.
Pharmacokinetics. After oral administration torasemid quickly and almost it is completely absorbed, the C max in blood plasma is reached by in 1–2 h. More than 90% of a torasemid contact proteins of blood plasma.
Distribution. Linking of a torasemid with blood proteins — more than 99%. The volume of distribution of a torasemid is 12–15 l. At patients with cirrhosis the volume of distribution almost doubles.
Removal. T ½ torasemida makes about 4 h. Process of removal is provided with metabolism in a liver (about 80% of the general clearance) and discharge kidneys (patients have about 20% with normal function of kidneys) due to removal of connection through proximal tubules with urine.
At patients with dekompensirovanny heart failure hepatic and renal clearance decrease, T ½ and AUC are extended.
renal clearance of a torasemid is considerably reducedAt patients with a renal failure, the indicator of the general clearance significantly does not change. The necessary diuretic effect at this group of patients is provided with increase in dosing.
Indication
Hypostases caused by stagnant heart failure, diseases of kidneys or a liver.
Essentsialnaya AG (as monotherapy or in a combination with other antihypertensive drugs).
Use
Pill should be taken, without chewing and without crushing, irrespective of consumption of food and of time of day, washing down with a small amount of liquid.
Stagnant heart failure. The general initial dose makes 10–20 mg of 1 times a day.
in the absence of necessary diuretic action needs to double a dose (20–40 mg/days) before achievement of necessary effect.
Chronic kidney disease. The general initial dose makes 20 mg of 1 times a day.
in the absence of necessary diuretic action should double a dose (40 mg/days) before achievement of necessary effect.
Cirrhosis. The general initial dose makes 5–10 mg of 1 times a day at the combined use with the medicaments antagonists of Aldosteronum or diuretics promoting a potassium delay in an organism. In the absence of necessary diuretic action it is necessary to raise a dose twice (10–20 mg/days) to achievement of necessary effect.
is not presentData on single dose in doses of 40 mg/days.
Essential hypertensia. The recommended initial dose makes 2.5 mg of a torasemid of 1 times a day. The maximum efficiency is reached after 12 weeks of continuous treatment.
If it is necessary for, the dose can be raised to 5 mg/days. It is known that increase in a dose of more than 5 mg/days does not lead to decrease in the ABP.
In case of need should perform complex therapy with other antihypertensive drugs.
Patients of advanced age do not need special selection of a dose.
increase in dosing for achievement of necessary diuretic effect in connection with reduced clearance of a torasemid can be required by Patients with a renal failure.
to Patients with a heavy abnormal liver function needs to be considered that the increased renal clearance of a torasemid can be followed by decrease in removal of ions of sodium.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to a torasemid or excipients of drug, sulphonylurea derivatives. renal failure with an anury, a hepatic coma, precoma, arterial hypotension, arrhythmia, a lactose intolerance or disturbance of absorption of glucose galactose. period of pregnancy and feeding by a breast.
Side effectsSide effects on the frequency of emergence classify
by such categories: very often (1/10), it is frequent (1/100, 1/10), sometimes (1/1000, 1/100), is rare (1/10,000, 1/1000), is very rare (1/10,000), including separate messages.
from a metabolism: sometimes — a hypercholesterolemia, a lipidemia, a polydipsia.
from nervous system: often — dizziness, a headache, drowsiness; sometimes — spasms of the lower extremities.
from a cardiovascular system: sometimes — premature ventricular contraction, the accelerated heartbeat, tachycardia, hyperaemia of the person.
from a respiratory system: sometimes — nasal bleedings.
from a GIT: often — diarrhea; sometimes — an abdominal pain, a meteorism.
from an urinary system: often — increase in frequency of urination, a polyuria, a night polyuria; sometimes — desires to urination.
General disturbances: sometimes — thirst, weakness, fatigue, superactivity, nervousness.
Change of laboratory indicators: sometimes — decrease in level of thrombocytes.
Other side reactions can be shown byin the form of nausea, vomiting, a hyperglycemia, a hyperuricemia, a hypovolemia, arterial hypotension, impotence, thromboses, skin reactions, a syncope.
toSpecial instructions
toIn an initiation of treatment the control at the patient of electrolytic exchange — hypopotassemias is necessary, for a hyponatremia, hypovolemia and disturbances of urination.
toAt long treatment torasemidy recommends regular monitoring of electrolytic balance, level of glucose, uric acid, creatinine and lipids of blood.
torecommends careful monitoring of patients with a tendency to a hyperuricemia and gout.
needs to control carbohydrate metabolism at patients with a latent and severe form of diabetes.
should use the Drug Trigrim with extra care to patients with liver diseases which are followed by cirrhosis and ascites as sudden changes of water and electrolytic balance can lead to a hepatic coma. Patients of this group need to carry out therapy using Trigrim (as well as other diuretics) in the conditions of a hospital. For prevention of a hypopotassemia and a metabolic acidosis it is necessary to appoint medicament with the medicaments antagonists of Aldosteronum or medicaments promoting a potassium delay in an organism.
After reception of a torasemid were noted by the ototoxicity phenomena (sonitus and hearing losses) having reversible character, but direct link with use of medicament is not established.
When prescribing diuretics needs to control carefully clinical symptoms of disturbance of electrolytic balance, a hypovolemia, an extrarenal azotemia and other disturbances which can be shown in the form of dryness in a mouth, thirst, weakness, slackness, drowsiness, excitement, muscular pain or spasms, a myasthenia, hypotonia, an oliguria, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting. The excessive diuresis can become the cause of dehydration of an organism, lead to decrease to OCK, a thrombogenesis and an embolism of blood vessels, especially at patients of advanced age.
to Patients with disturbance of water and electrolytic balance needs to stop use of medicament and after elimination of side effects to restore therapy by Trigrim, since lower doses.
At patients with cardiovascular diseases, especially in case of intake of cardiac glycosides, the hypopotassemia arising at intake of diuretics can increase risk of developing arrhythmia.
needs to carry out byWhen prescribing medicament regular laboratory control of indicators of level of potassium and other electrolytes in blood plasma.
Use during pregnancy and feeding by a breast. There are no data on action of a torasemid on an embryo and a fruit of the person and also about penetration into breast milk therefore it is not recommended to accept torasemid during pregnancy and feeding by a breast.
Children. Safety given relatively and efficiency of use of a torasemid for children are absent therefore it is not necessary to appoint the medicament Trigrim of this age category of patients.
Ability to influence speed of response at control of vehicles or work with other mechanisms. Drug can change the speed of response of the person, reducing it during control of vehicles or work with other mechanisms, especially at simultaneous use with alcohol. Therefore it is necessary to avoid control of vehicles or work with potentially dangerous mechanisms during medicament treatment.
byInteraction
At simultaneous use of a trigrim with blockers of β-adrenoceptors, blockers of calcium channels, inhibitors apf, foxglove drugs, organic nitrates did not reveal new or unforeseen by-effects.
Trigrim's Reception does not affect ability of linking of glibenclamide or warfarin with proteins of blood plasma, does not change also anticoagulative properties of a fenprokumon, does not affect pharmacokinetic characteristics of digoxin or a karvedilol. In case of the combined use of a torasemid with Spironolactonum the renal clearance of the last decreases, however there is no need for correction of doses of drugs.
At the combined use with salicylates in high doses the toxic effect of salicylates increases. NPVP (including acetylsalicylic acid) at the combined use with medicament and other diuretics which action point — a Henle's loop, can break function of kidneys.
At the combined use with indometacin the diuretic action of a torasemid (only on condition of limited intake of sodium in an organism partially is suppressed with— 50 mekv / days), in the conditions of normal intake of sodium (150 mekv / days) the similar phenomena are noted.
Cimetidinum, Spironolactonum do not change efficiency of a torasemid.
Digoksin can increase AUC of a torasemid by 50%, however in dose adjustment there is no need.
Combined therapy with Colestyraminum is recommended to be carried out byto different periods.
At a concomitant use with probenetsidy the diuretic action of a torasemid decreases.
Diuretics reduce renal clearance of lithium, increasing its toxic action, and can increase expressiveness of ototoksichesky effect of aminoglycosides and Acidum etacrynicum, especially at patients with a renal failure. The research of these interactions with Trigrim was not conducted.
Overdose
Is absent a typical picture of intoxication.
Symptoms: strengthening of a diuresis with threat of dehydration and loss of electrolytes that can result in drowsiness and confusion of consciousness, arterial hypotension, cardiovascular insufficiency.
Treatment. There is no special antidote. It is necessary to lower a dose or to stop use of a torasemid and at the same time to carry out completion of volume of liquid and correction of electrolytes.
Storage conditions
B the dry, protected from light place at a temperature not above 25 °C. to store out of children's reach.
Specifications
| Characteristics | |
| Active ingredients | Torasemid |
| Amount of active ingredient | 10 mg |
| Applicant | Polpharma |
| Code of automatic telephone exchange | C03CA04 Torasemid |
| Interaction with food | It doesn't matter |
| Light sensitivity | Not sensitive |
| Market status | The branded generic |
| Origin | Chemical |
| Prescription status | According to the prescription |
| Primary packing | blister |
| Producer | PHARMACEUTICAL. POLFARM S.A PLANT. |
| Quantity in packing | 30 tablets (3 blisters on 10 pieces) |
| Release form | tablets for internal use |
| Route of administration | Oral |
| Sign | Import |
| Storage temperature | from 5 °C to 25 °C |
| Trade name | Trigrim |














































